how do brakes work on a train
The power part comes from air stored in a reservoir on each car. Dynamic brakes use the kinetic energy of a trains turning wheels to create electrical energy which causes the train to decelerate.
The brake allows the locomotive to slow and stop.
. Friction rubbing between the rough ground and the grip on your soles slows you down converting your kinetic energy into heat energy do it long enough and your shoes will get hot. Trains that hover just above the tracks are actually possible due to magnetic levitation or maglev for short. These trains use powerful magnets to stay in the air.
Dynamic braking is the method of train braking whereby the kinetic energy of a moving train is used to generate electric current at the locomotive traction motors. A railway brake is a type of brake used on the cars of railway trains to enable deceleration control acceleration or to keep them immobile when parked. How could a train possibly move along the tracks without wheels.
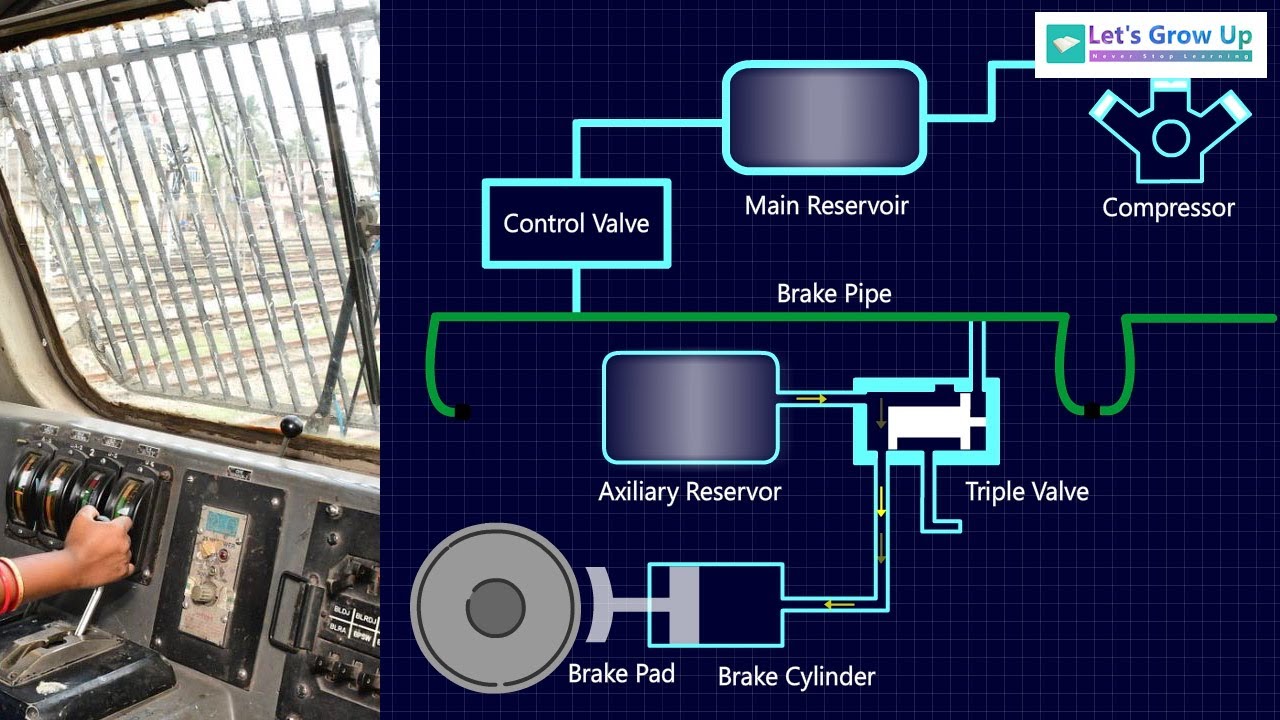
When the train reaches flat land the engineer disengages the dynamic brake which turns the fans off fires up the prime mover and begins sending current to the traction motors again. A What are independent brakesb What are auto brakesc What re dynamic brakesd. The compressed air is released into the brake cylinders through triple valves which are controlled by air pressure from the train pipe.
The reversing gear enables the locomotive to back up. Before air brakes trains used a primitive brake system that required an operator or brakeman in each car to apply a hand brake at the signal of the train director or engineer. Magnets generate a magnetic fieldThis magnetic field can push or pull on other nearby.
The AB valve is used to route air from the reservoirs auxiliary and emergency to the brake cylinder. Depends on the train and location. Brakes on vehicles work pretty much the same way with shoes that press rubber pads brake blocks against discs mounted to the wheels.
In your car slamming on the brake pedal transfers your foot pressurethrough brake fluidto a piston which clamps a. Us freight railroad brakes use a pressurized air line to supply reservoirs on each car. When you push the function key to turn on the dynamic brakes on a DCC-sound-equipped model locomotive the sound you hear is those fans kicking in.
Does a train without wheels sound crazy. Because it consists of electrical energy dynamic braking can be finely adjusted downward more so than air brakes. When there is a dip in pressure in that line from an application or a hose break it trips a valve on the reservoir and sends a corresponding increase in air pressure to the brake cylinders.
The train line will be at 64 psi the main reservoir will be at 64 psi and the brake cylinder will also be about 64 psi. Each reservoir on each car is charged up by air supplied from the locomotive through the brake pipe. The dynamic brake grids consume electricity that make the traction motor less able to turn and thus slow down.
The air brake system on a train works by the linkage of all the carriages or trucks from the engine and works by not pushing on the brakes but instead it holds them off until the pedal is pressed and the air is prevented and the brakes lock on. While the train is coasting the engineer using an eight-notch controller similar to the throttle energizes the traction-motor fields causing the motors to act as generators. Normally with the train rolling along and the brakes released the locomotive will be maintaining 90 psi in the brake pipe and the reservoirs will be charged up to 90 psi too.
When the operator of the train activates the electro-pneumatic brakes the system uses a mechanical connection to apply pressure to the wheels through the brake block components of the train. If the train accidentally uncouples the brakes will automatically apply fully-since all of the brake pipe pressure will be vented to the atmosphere through the disconnected pipe. Those brakes are bailed off using the independent locomotive brake lever.
Operators control the train by using the throttle reversing gear and brake. Dynamic brakes use the kinetic energy of a trains turning wheels to create electrical energy which causes the train to decelerate. This inefficient manual system was replaced by direct air-brake systems which used an air compressor to feed air through a brake pipe into air tanks on each car.
The brake components include a brake cylinder brake shoes a dual air reservoir and a control or AB valve. It works like this. When releasing the automatic brake the brakes on the cars back off but the brakes on the locomotive stay applied.
Each rail car has its own brake system. 26 psi x 25 65 psi. While the basic principle is similar to that on road vehicle usage operational features are more complex because of the need to control multiple linked carriages and to be effective on vehicles left without a prime mover.
Maximum service braking is reached when equilization between the train line auxilary reservoir and brake cylinder is reached. From a 90 psi train line pressure that happens when about 26 psi is drawn off. Unlike truck brakes train brakes are normally off or unapplied.
In some ways a trains air brake is a lot like the brake on your car. Each cars has a set of brakes air lines and cylinders which regulate the brakes on each car by responding to the commands of the engineer. Brake cylinder of each car causes the brakes to move away from the wheels.
When air brakes were first implemented in the 19th century their use revolutionized railroad operation making it a safer more effective way to travel. The throttle controls the speed of the locomotive. The brakes apply whenever the air pressure in the brake pipe drops.
An important component of steam cylinders is the piston and the Piston rod is what propels the brake transfers the brake force through a system of rods into the brake blocks ts motion by the steam admitted the piston rod transfers the brake force via a system of rods to Through the use of an air leakage valve Entwsserungsventil steam generated both expand and condensed is. In this small tutorial we go through the basics of how train brakes work. This is made possible by an air line that spans the entire length of the train.
When using the automatic brake with a train both the car brakes and locomotive brakes are applied at the same time. Regardless of the type locomotives use air brakes and hand brakes to stop the engine. The dynamic brake grids consume electricity that make the traction motor less able to turn and.
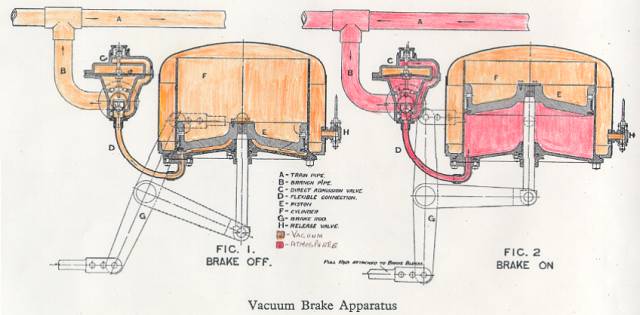
Vacuum Brakes The Railway Technical Website Prc Rail Consulting Ltd
Vacuum Brakes The Railway Technical Website Prc Rail Consulting Ltd

What Is Train Air Brake Trainairbrake Introduction Of Train Braking System Lhb Train Brake Youtube
Electro Pneumatic Brakes The Railway Technical Website Prc Rail Consulting Ltd
A Life Cycle Approach To Braking Costs International Railway Journal
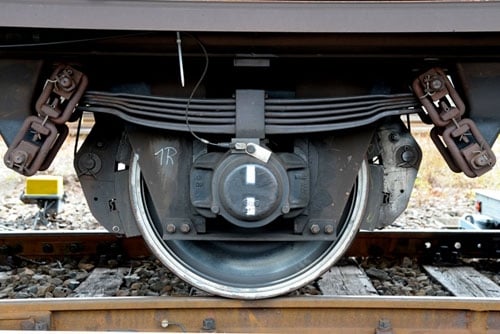
South Devon Railway Brake Cylinder
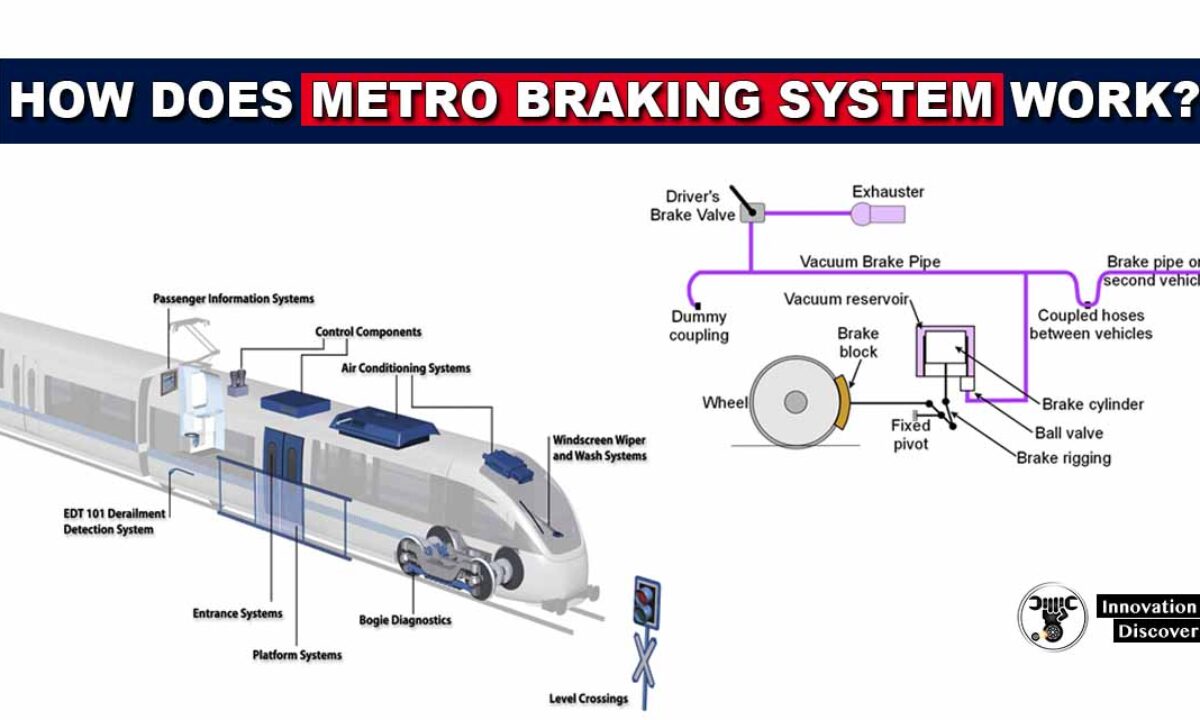
What Type Of Braking System Used In Metro Trains How Does Metro
Electro Pneumatic Brakes The Railway Technical Website Prc Rail Consulting Ltd
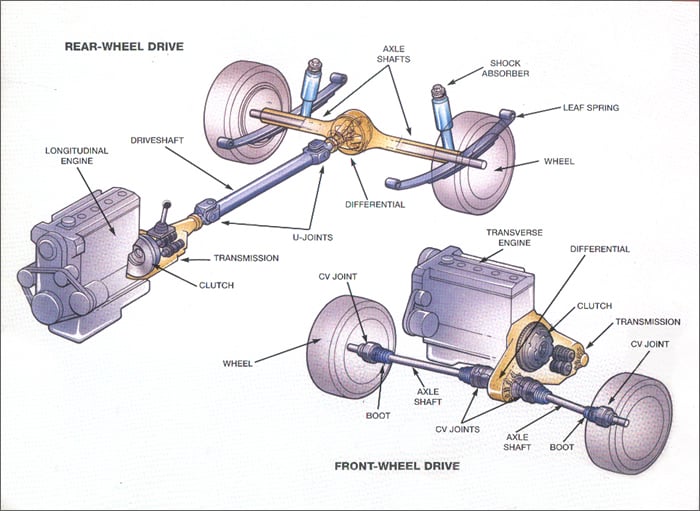
The Drive Train Hydraulic Brake System Steering System Schoolworkhelper
Vacuum Brakes The Railway Technical Website Prc Rail Consulting Ltd
How Does The Air Brake System Work In A Train Quora

Train Braking Performance Determination Global Railway Review

Air Brakes And Locomotive Connections Youtube
How Does The Air Brake System Work In A Train Quora
How Does The Air Brake System Work In A Train Quora
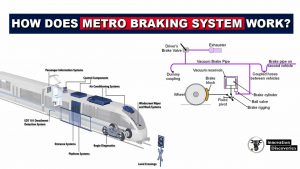
What Type Of Braking System Used In Metro Trains How Does Metro

Couplers Brakes The Transcontinental Railroad
What Is A Vacuum Braking System Quora
Bogies The Railway Technical Website Prc Rail Consulting Ltd
.jpg)